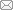
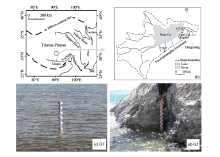
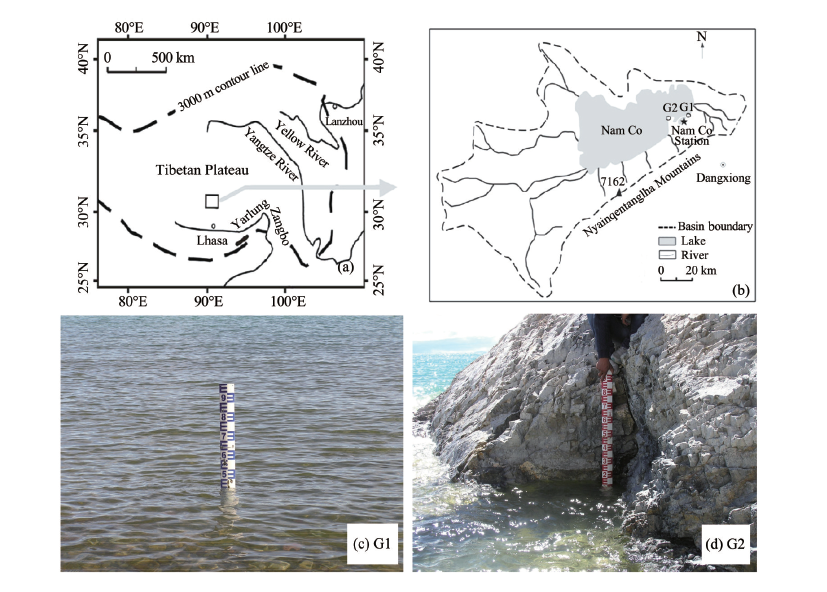
Sciences in Cold and Arid Regions ›› 2020, Vol. 12 ›› Issue (6): 430–435.doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1226.2020.00430
A note on the lake level variations of Nam Co, south-central Tibetan Plateau from 2005 to 2019
- 1.Key Laboratory of Tibetan Environment Changes and Land Surface Processes, Institute of Tibetan Plateau Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100101, China
2.University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
| Bai H, Xie J, Li D, 2001. The principal feature of Qinghai-Xizang Plateau monsoon variation in 40 years. Plateau Meteorology, 20(1): 22-27. (in Chinese) | |
| Bian D, Yang Z, Li L, et al., 2006. The response of lake area change to climate variations in north Tibetan Plateau during last 30 years. Acta Geographica Sinica, 61(5): 510-518. (in Chinese) | |
|
Crétaux JF, Jelinski W, Calmant S, et al., 2011. SOLS: A lake database to monitor in the Near Real Time water level and storage variations from remote sensing data. Advances in Space Research, 47(9): 1497-1507. DOI: 10.1016/j.asr. 2011.01.004.
doi: 10.1016/j.asr. 2011.01.004 |
|
| Chu D, Pu Q, Wang D, et al., 2012. Water level variations of YamzhoYumco Lake in Tibet and the main driving forces. Journal of Mountain Science, 30(2): 239-247. (in Chinese) | |
|
Gao L, Liao J, Shen G, 2013. Monitoring lake-level changes in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau using radar altimeter data (2002-2012). Journal of Applied Remote Sensing, 7(1): 073470. DOI: 10.1117/1.JRS.7.073470.
doi: 10.1117/1.JRS.7.073470 |
|
| Ge S, Zonggha, 2005. A preliminary study on the change of lake areas in western Naqu, Tibet. Tibetan Science and Technology, 144: 14-18. (in Chinese) | |
|
Jacob T, Wahr J, Pfeffer WT, et al., 2012. Recent contributions of glaciers and ice caps to sea level rise. Nature, 482: 514-518. DOI: 10.1038/nature10847.
doi: 10.1038/nature10847 |
|
|
Kropáček J, Braun A, Kang S, et al., 2012. Analysis of lake level changes in Nam Co in central Tibet utilizing synergistic satellite altimetry and optical imagery. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 17: 3-11. DOI: 10.1016/j.jag.2011.10.001.
doi: 10.1016/j.jag.2011.10.001 |
|
|
Lei Y, Yao T, Bird BW, et al., 2013. Coherent lake growth on the central Tibetan Plateau since the 1970s: Characterization and attribution. Journal of Hydrology, 483: 61-67. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2013.01.003.
doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2013.01.003 |
|
|
Lei Y, Yao T, Yang K, et al., 2017. Lake seasonality across the Tibetan Plateau and their varying relationship with regional mass changes and local hydrology. Geophysical Research Letters, 44: 892-900. DOI: 10.1002/2016GL072062.
doi: 10.1002/2016GL072062 |
|
|
Li X, Xu H, Sun Y, et al., 2007. Lake-level change and water balance analysis at Lake Qinghai, west China during recent decades. Water Resources Management, 21: 1505-1516. DOI: 10.1007/s11269-006-9096-1.
doi: 10.1007/s11269-006-9096-1 |
|
|
Liu J, Wang Z, Yu S, et al., 2009. Climate warming and growth of high-elevation inland lakes on the Tibetan Plateau. Global and Planetary Change, 67: 209-217. DOI: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2009.03.010.
doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2009.03.010 |
|
| Lu A, Yao T, Wang L, et al., 2005. Study on the fluctuations of typical glaciers and lakes in the Tibetan Plateau using remote sensing. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 27(6): 783-792. (in Chinese) | |
|
Phan VH, Lindenbergh R, Menenti M, 2012. ICESat derived elevation changes of Tibetan lakes between 2003 and 2009. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 17: 12-22. DOI: 10.1016/j.jag.2011. 09.015.
doi: 10.1016/j.jag.2011. 09.015 |
|
|
Song C, Huang B, Ke L, et al., 2014. Seasonal and abrupt changes in the water level of closed lakes on the Tibetan Plateau and implications for climate impacts. Journal of Hydrology, 514: 131-144. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2014. 04.018.
doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2014. 04.018 |
|
|
Song C, Ye Q, Cheng X, 2015a. Shifts in water-level variation of Namco in the central Tibetan Plateau from ICESat and CryoSat-2 altimetry and station observations. Science Bulletin, 60(14): 1287-1297. DOI: 10.1007/s11434-015-0826-8.
doi: 10.1007/s11434-015-0826-8 |
|
|
Song C, Ye Q, Sheng Y, et al., 2015b. Combined ICESat and CryoSat-2 altimetry for accessing water level dynamics of Tibetan lakes over 2003-2014. Water, 7(9): 4685-4700. DOI: 10.3390/w7094685.
doi: 10.3390/w7094685 |
|
|
Wang X, Gong P, Zhao Y, et al., 2013. Water-level changes in China's large lakes determined from ICESat/GLAS data. Remote Sensing of Environment, 132: 131-144. DOI: 10. 1016/j.rse.2013.01.005.
doi: 10. 1016/j.rse.2013.01.005 |
|
|
Wu H, Wang N, Jiang X, et al., 2014. Variations in water level and glacier mass balance in Nam Co lake, Nyainqentanglha range, Tibetan Plateau, based on ICESat data for2003-09. Annuals of Glaciology, 55(66): 239-247. DOI: 10.3189/2014AoG66A100.
doi: 10.3189/2014AoG66A100 |
|
|
Yang K, Yao F, Wang J, et al., 2017. Recent dynamics of alpine lakes on the endorheic Changtang Plateau from multi-mission satellite data. Journal of Hydrology, 552: 633-645. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2017.07.024.
doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2017.07.024 |
|
|
Zhang B, Wu Y, Zhu L, et al., 2011. Estimation and trend detection of water storage at Nam Co Lake, central Tibetan Plateau. Journal of Hydrology, 405: 161-170. DOI: 10. 1016/j.jhydrol.2011.05.018.
doi: 10. 1016/j.jhydrol.2011.05.018 |
|
|
Zhang G, Xie H, Kang S, et al., 2011. Monitoring lake level changes on the Tibetan plateau using ICESat altimetry data (2003-2009). Remote Sensing of Environment, 115: 1733-1742. DOI: 10.1016/j.rse.2011.03.005.
doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2011.03.005 |
|
|
Zhang G, Yao T, Xie H, et al., 2013. Increased mass over the Tibetan Plateau: From lakes or glaciers? Geophysical Research Letters, 40: 2125-2130. DOI: 10.1002/grl.50462.
doi: 10.1002/grl.50462 |
|
|
Zhang G, Yao T, Shum CK, et al., 2017. Lake volume and groundwater storage variations in Tibetan Plateau's endorheic basin. Geophysical Research Letters, 44: 5550-5560. DOI: 10.1002/2017GL073773.
doi: 10.1002/2017GL073773 |
|
|
Zhang G, Chen W, Xie H, 2019. Tibetan Plateau's lake level and volume changes from NASA's ICESat/ICESat-2 and Landsat missions. Geophysical Research Letters, 46: 13107-13118. DOI: 10.1029/2019GL085032.
doi: 10.1029/2019GL085032 |
|
|
Zhou S, Kang S, Chen F, et al., 2013. Water balance observations reveal significant subsurface water seepage from Lake Nam Co, south-central Tibetan Plateau. Journal of Hydrology, 491: 89-99. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2013. 03.030.
doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2013. 03.030 |
| No related articles found! |