Sciences in Cold and Arid Regions ›› 2021, Vol. 13 ›› Issue (3): 268–270.doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1226.2021.21034.
• • 上一篇
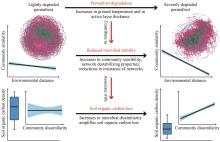
Linkages between soil microbial stability and carbon storage in the active layer under permafrost degradation
ShengYun Chen1,2,MingHui Wu1,3,Yu Zhang2,Kai Xue3
- 1.Cryosphere and Eco-Environment Research Station of Shule River Headwaters, State Key Laboratory of Cryospheric Science, Northwest Institute of Eco-Environment and Resources, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Lanzhou, Gansu 730000, China
2.Long-term National Scientific Research Base of the Qilian Mountain National Park, Xining, Qinghai 810000, China
3.University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
|
Chen SY, Liu WJ, Qin X, et al., 2012. Response characteristics of vegetation and soil environment to permafrost degradation in the upstream regions of the Shule River Basin. Environmental Research Letters, 7(4): 045406. DOI: 10.1088/1748-9326/7/4/045406.
doi: 10.1088/1748-9326/7/4/045406 |
|
| Chen YL, Deng Y, Ding JZ, et al., 2017. Distinct microbial communities in the active and permafrost layers on the Tibetan Plateau. Molecular Ecology, 26(23): 6608-6620. . | |
| DeConto RM, Galeotti S, Pagani M, et al., 2012. Past extreme warming events linked to massive carbon release from thawing permafrost. Nature, 484(7392): 87-91. | |
| Hale L, Feng WT, Yin HQ, et al., 2019. Tundra microbial community taxa and traits predict decomposition parameters of stable, old soil organic carbon. The ISME Journal, 13(12): 2901-2915. . | |
| Liu FT, Kou D, Abbott BW, et al., 2019. Disentangling the effects of climate, vegetation, soil and related substrate properties on the biodegradability of permafrost-derived dissolved organic carbon. Journal of Geophysical Research: Biogeosciences, 124(11): 3377-3389. . | |
| Schuur EAG, McGuire AD, Schädel C, et al., 2015. Climate change and the permafrost carbon feedback. Nature, 520(7546): 171-179. | |
| Shur YL, Jorgenson MT, 2007. Patterns of permafrost formation and degradation in relation to climate and ecosystems. Permafrost and Periglacial Processes, 18(1): 7-19. | |
| Wang TH, Yang DW, Yang YT, et al., 2020. Permafrost thawing puts the frozen carbon at risk over the Tibetan Plateau. Science Advances, 6(19): eaaz3513. | |
| Wu MH, Chen SY, Chen JW, et al., 2021. Reduced microbial stability in the active layer is associated with carbon loss under alpine permafrost degradation. Proceedings of the National Academy of the Sciences of the United States of America, 118(25): e2025321118. . | |
| Xue K, Yuan MM, Shi ZJ, et al., 2016. Tundra soil carbon is vulnerable to rapid microbial decomposition under climate warming. Nature Climate Change, 6(6): 595-600. | |
| Yang MX, Nelson FE, Shiklomanov NI, et al., 2010. Permafrost degradation and its environmental effects on the Tibetan Plateau: A review of recent research. Earth-Science Review, 103(1-2): 31-44. | |
| Zou DF, Zhao L, Sheng Y, et al., 2017. A new map of the permafrost distribution on the Tibetan Plateau. The Cryosphere, 11(6): 2527-2542. |
| No related articles found! |