Sciences in Cold and Arid Regions ›› 2019, Vol. 11 ›› Issue (2): 139–149.doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1226.2019.00139.
• • 上一篇
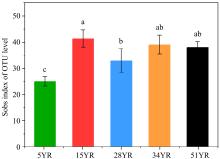
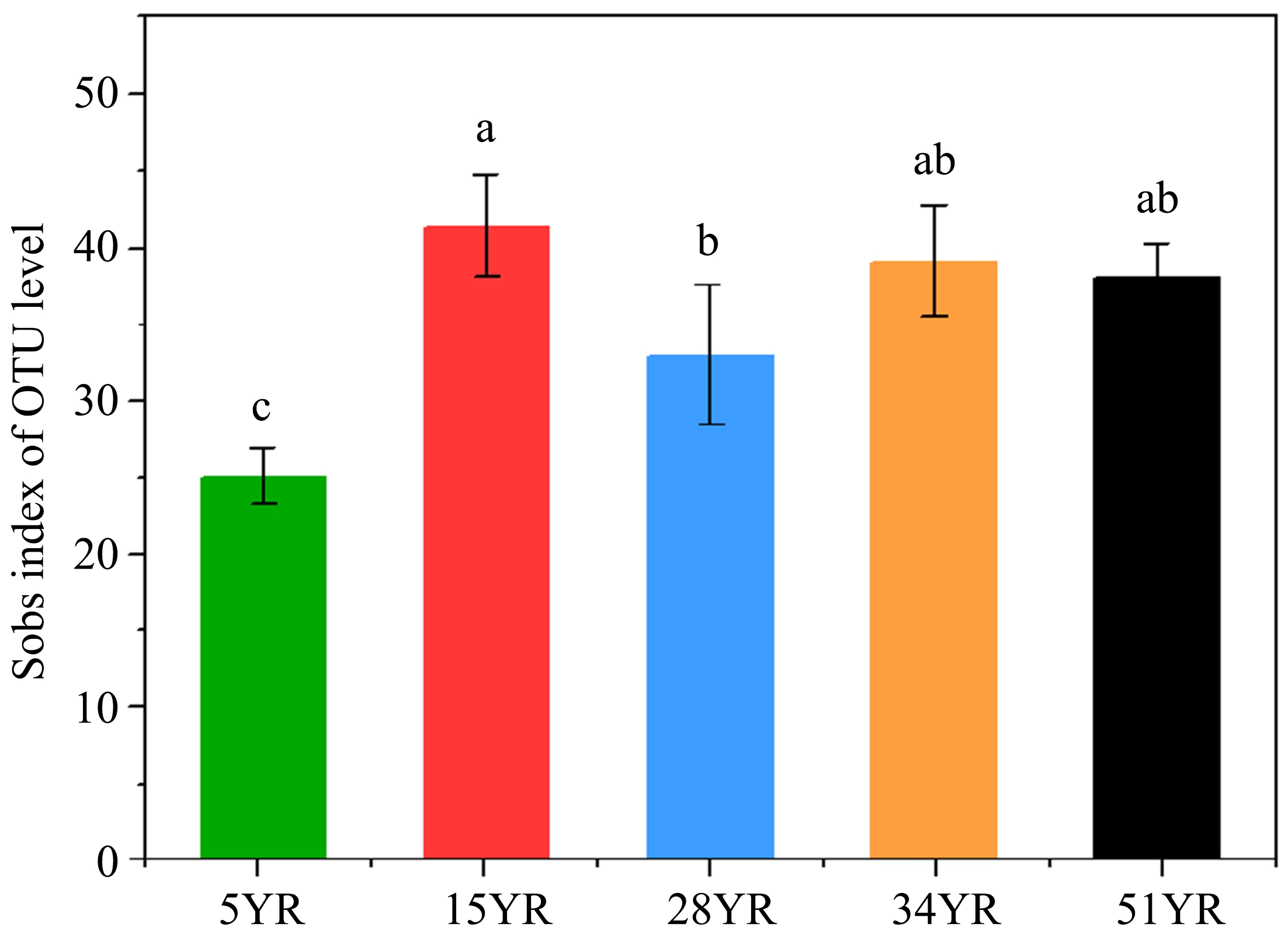
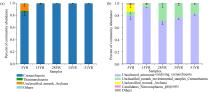
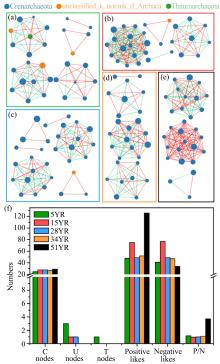
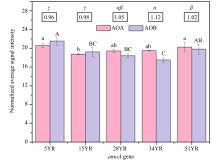
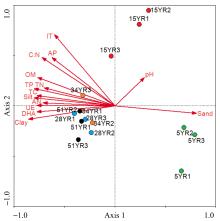
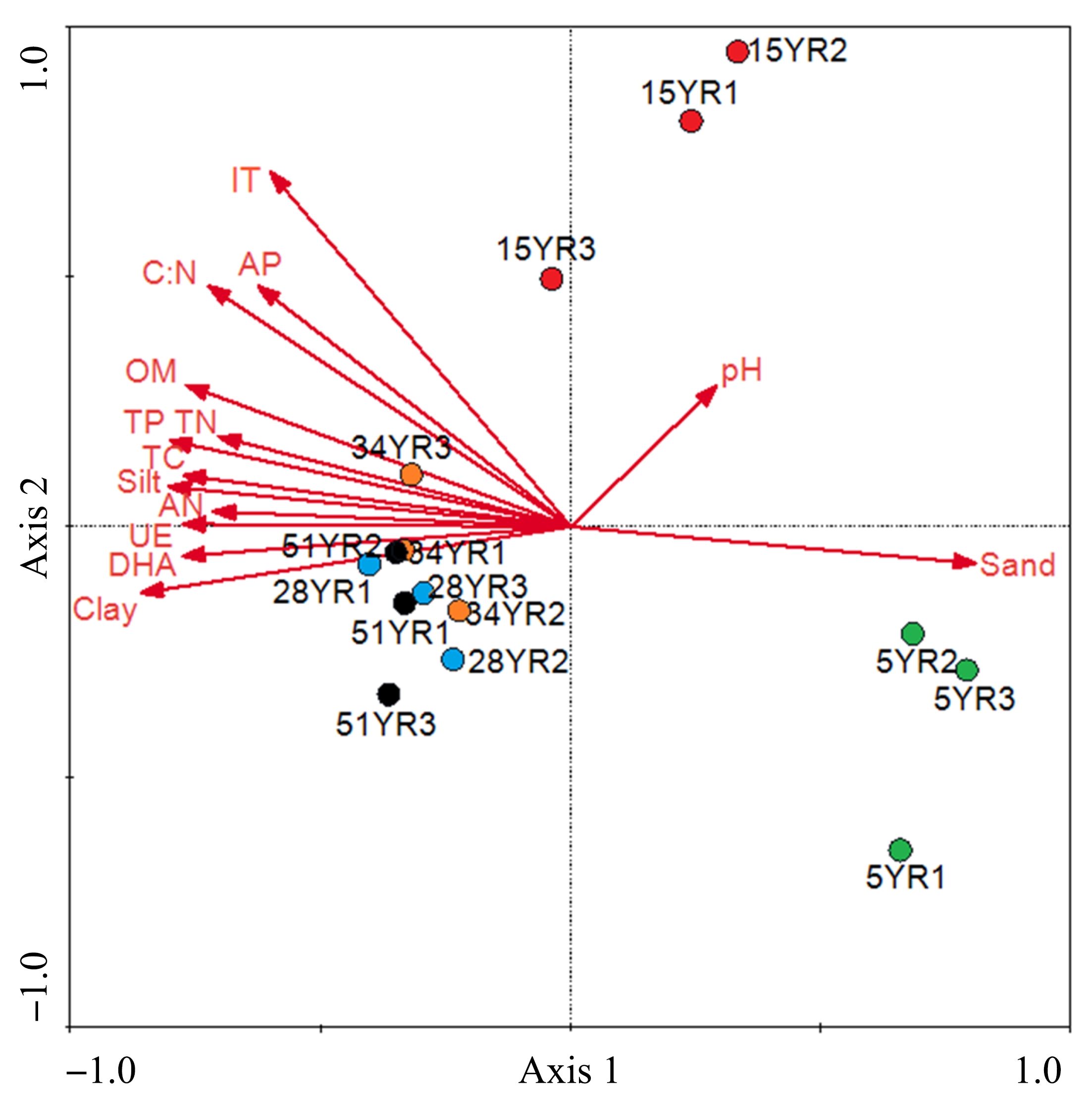
Shifts in community structure and function of ammonia-oxidizing archaea in biological soil crusts along a revegetation chronosequence in the Tengger Desert
LiNa Zhao1,2,4,XinRong Li1,2,ShiWei Yuan3,4,YuBing Liu1,2( )
)
- 1. Shapotou Desert Research and Experiment Station, Northwest Institute of Eco-Environment and Resources, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Lanzhou, Gansu 730000, China
2. Key Laboratory of Stress Physiology and Ecology in Cold and Arid Regions of Gansu Province, Northwest Institute of Eco-Environment and Resources, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Lanzhou, Gansu 730000, China
3. Key Laboratory of Remote Sensing of Gansu Province, Northwest Institute of Eco-Environment and Resources, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Lanzhou, Gansu 730000, China
4. University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
|
Abed RM , Al Kharusi S , Schramm A , et al . , 2010. Bacterial diversity, pigments and nitrogen fixation of biological desert crusts from the Sultanate of Oman. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 72: 418−428. DOI: 10.1111/j.1574-6941.2010. 00854.x.
doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6941.2010. 00854.x |
|
|
Aitkenhead JA , Mcdowell WH , 2000. Soil C:N ratio as a predictor of annual riverine DOC flux at local and global scales. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 14(1): 127−138. DOI: 10.1029/1999GB900083.
doi: 10.1029/1999GB900083 |
|
|
Andrés P , Moore JC , Simpson RT , et al . , 2016. Soil food web stability in response to grazing in a semiarid prairie: the importance of soil textural heterogeneity. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 97: 131−143. DOI: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2016. 02.014.
doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2016. 02.014 |
|
| Belnap J , 2003. Factors influencing nitrogen fixation and nitrogen release in biological soil crusts. In: Belnap J, Lange OL (eds.). Biological Soil Crusts: Structure, Function, and Management.Springer, Berlin, pp.241−261. | |
| Belnap J , Weber B , Büdel B , 2016. Biological soil crusts as an organizing principle in drylands. In: Weber B, Büdel B, Belnap J (eds.).Biological Soil Crusts: an Organizing Principle in Drylands.Springer, Cham, pp. 3−13. | |
| Casida LE Jr , Klein DA , Santoro T , 1964. Soil dehydrogenase activity. Soil Science, 98: 371−376. | |
| Chen Z , Wu WL , Shao XM , et al . , 2015. Shifts in abundance and diversity of soil ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and archaea associated with land restoration in a semi-arid ecosystem. PLoS One, 10(7): e0132879. | |
| Di HJ , Cameron KC , Shen JP , et al . , 2009. Nitrification driven by bacteria and not archaea in nitrogen-rich grassland soils. Nature Geoscience, 2: 621−624. | |
|
Erguder TH , Boon N , Wittebolle L , et al . , 2009. Environmental factors shaping the ecological niches of ammonia-oxidizing archaea. FEMS Microbiology Reviews, 33: 855−869. DOI: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2009.00179.x.
doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2009.00179.x |
|
|
Feng K , Zhang ZJ , Cai W , et al . , 2017. Biodiversity and species competition regulate the resilience of microbial biofilm community. Molecular Ecology, 26: 6170−6182. DOI: 10.1111/mec.14356.
doi: 10.1111/mec.14356 |
|
|
Fierer N , Jackson RB , 2006. The diversity and biogeography of soil bacterial communities. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 103: 626−631. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0507535103.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.0507535103 |
|
| Hagberg AA , Schult DA , Swart PJ , 2008. Exploring network structure, dynamics, and function using NetworkX. In: Varoquaux G, Vaught T, Millman J (eds.). The 7th Python in Science Conference (SciPy2008)Pasadena, CA, pp. 11−15. | |
|
Hallam SJ , Mincer TJ , Schleper C , et al . , 2006. Pathways of carbon assimilation and ammonia oxidation suggested by environmental genomic analyses of marine Crenarchaeota. PLoS Biology, 4: e95. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0040095.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0040095 |
|
|
Harris J , 2009. Soil microbial communities and restoration ecology: facilitators or followers? Science, 325: 573−574. DOI: 10.1126/science.1172975.
doi: 10.1126/science.1172975 |
|
|
Hayden HL , Drake J , Imhof M , et al . , 2010. The abundance of nitrogen cycle genes amoA and nifH depends on land-uses and soil types in South-Eastern Australia. Soil Biology AND Biochemistry, 42: 1774−1783. DOI: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2010.06.015.
doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2010.06.015 |
|
|
He M , Dijkstra FA , Zhang K , et al . , 2016. Influence of life form, taxonomy, climate, and soil properties on shoot and root concentrations of 11 elements in herbaceous plants in a temperate desert. Plant and Soil, 398: 1−12. DOI: 10.10 07/s11104-015-2669-0.
doi: 10.10 07/s11104-015-2669-0 |
|
|
Jesus ED , Marsh TL , Tiedje JM , et al . , 2009. Changes in land use alter the structure of bacterial communities in western amazon soils. ISME Journal, 3: 1004−1011. DOI: 10.1038/ismej.2009.47.
doi: 10.1038/ismej.2009.47 |
|
|
Jiang X , Wu Y , Liu G , et al . , 2017. The effects of climate, catchment land use and local factors on the abundance and community structure of sediment ammonia-oxidizing microorganisms in Yangtze lakes. AMB Express, 7(1): 173. DOI: 10.1186/s13568-017-0479-x.
doi: 10.1186/s13568-017-0479-x |
|
|
Jin K , Sleutel S , Buchan D , et al . , 2009. Changes of soil enzyme activities under different tillage practices in the Chinese loess plateau. Soil and Tillage Research, 104(1): 115−120. DOI: 10.1016/j.still.2009.02.004.
doi: 10.1016/j.still.2009.02.004 |
|
|
Kowalchuk GA , Stephen JR , 2001. Ammonia-oxidizing bacteria: a model for molecular microbial ecology. Annual Review of Microbiology, 55: 485−529. DOI: 10.1146/annurev.micro.55.1.485.
doi: 10.1146/annurev.micro.55.1.485 |
|
|
López-Lozano NE , Heidelberg KB , Nelson WC , et al . , 2013. Microbial secondary succession in soil microcosms of a desert oasis in the Cuatro Cienegas Basin, Mexico. PeerJ, 1: e47. DOI: 10.7717/peerj.47.
doi: 10.7717/peerj.47 |
|
|
Leininger S , Urich T , Schloter M , et al . , 2006. Archaea predominate among ammonia-oxidizing prokaryotes in soils. Nature, 442: 806−809. DOI: 10.1038/nature04983.
doi: 10.1038/nature04983 |
|
|
Li XR , Kong DS , Tan HJ , et al . , 2007. Changes in soil and vegetation following stabilisation of dunes in the southeastern fringe of the Tengger Desert, China. Plant and Soil, 300: 221−231. DOI: 10.1007/s11104-007-9407-1.
doi: 10.1007/s11104-007-9407-1 |
|
|
Li XR , Zhang P , Su YG , et al . , 2012. Carbon fixation by biological soil crusts following revegetation of sand dunes in arid desert regions of China: A four-year field study. Catena, 97: 119−126. DOI: 10.1016/j.catena.2012.05.009.
doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2012.05.009 |
|
|
Liu LC , Li SZ , Duan ZH , et al . , 2006. Effects of microbiotic crusts on dew deposition in the restored vegetation area at Shapotou, northwest China. Journal of Hydrology, 328: 331−337. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2005.12.004.
doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2005.12.004 |
|
|
Liu LC , Liu YB , Zhang P , et al . , 2017. Development of bacterial communities in biological soil crusts along a revegetation chronosequence in the Tengger Desert, northwest China. Biogeosciences, 14: 3801−3814. DOI: 10.5194/bg-14-3801-2017.
doi: 10.5194/bg-14-3801-2017 |
|
|
Mao Y , Yannarell AC , Mackie RI , 2011. Changes in N-transforming archaea and bacteria in soil during the establishment of bioenergy crops. PLoS One, 6: e24750. DOI: 10. 1371/journal.pone.0024750.
doi: 10. 1371/journal.pone.0024750 |
|
|
Martens-Habbena W , Berube PM , Urakawa H , et al . , 2009. Ammonia oxidation kinetics determine niche separation of nitrifying Archaea and Bacteria. Nature, 461: 976−979. DOI: 10.1038/nature08465.
doi: 10.1038/nature08465 |
|
|
Mayland HF , Mcintosh TH , 1966. Availability of biologically fixed atmospheric nitrogen-15 to higher plants. Nature, 209: 421−422. DOI: 10.1038/209421a0.
doi: 10.1038/209421a0 |
|
|
Moritsuka N , Izawa G , Katsura K , et al . , 2015. Simple method for measuring soil sand content by nylon mesh sieving. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 61: 501−505. DOI: 10.10 80/00380768.2015.1016864.
doi: 10.10 80/00380768.2015.1016864 |
|
| Nanjing Institute of Soil Research , 1980. Analysis of Soil Physicochemical Features. Shanghai Science and Technology Press, Shanghai, pp. 360. (in Chinese) | |
|
Neher DA , Lewins SA , Weicht TR , et al . , 2009. Microarthropod communities associated with biological soil crusts in the Colorado Plateau and Chihuahuan deserts. Journal of Arid Environments, 73: 672−677. DOI: 10.1016/j.jaridenv. 2009.01.013.
doi: 10.1016/j.jaridenv. 2009.01.013 |
|
| Nelson DW , Sommers LE , 1996. Total carbon, organic carbon and organic matter. Methods of Soil Analysis Part 3—chemical Methods, (methodsofsoilan3), pp. 961−1010. | |
|
Offre P , Kerou M , Spang A , et al . , 2014. Variability of the transporter gene complement in ammonia-oxidizing archaea. Trends in Microbiology, 22: 665−675. DOI: 10.10 16/j.tim.2014.07.007.
doi: 10.10 16/j.tim.2014.07.007 |
|
|
Ouyang Y , Norton JM , Stark JM , et al . , 2016. Ammonia-oxidizing bacteria are more responsive than archaea to nitrogen source in an agricultural soil. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 96: 4−15. DOI: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2016.01.012.
doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2016.01.012 |
|
| Parton WJ , Cole CV , Stewart JWB , et al ., 1989. Simulating regional patterns of soil C, N and P dynamics in the U.S. central grasslands region.In: Clarholm M, Bergström L (eds.).Ecology of Arable Land—Perspectives and Challenges .Kluwer Academic Publishers, Netherlands, pp. 99−108. | |
|
Prosser JI, Nicol GW , 2012. Archaeal and bacterial ammonia-oxidisers in soil: the quest for niche specialisation and differentiation. Trends in Microbiology, 20: 523−531. DOI: 10.1016/j.tim.2012.08.001.
doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2012.08.001 |
|
|
Raun WR , Johnson GV , 1999. Improving nitrogen use efficiency for cereal production. Agronomy Journal, 91: 357−363. DOI: 10.2134/agronj1999.00021962009100030001x.
doi: 10.2134/agronj1999.00021962009100030001x |
|
|
Rawls WJ , Pachepsky YA , Ritchie JC , et al . , 2003. Effect of soil organic carbon on soil water retention. Geoderma, 116: 61−76. DOI: 10.1016/S0016-7061(03)00094-6.
doi: 10.1016/S0016-7061(03)00094-6 |
|
|
Schleper C , Nicol GW , 2010. Ammonia-oxidising archaea-physiology, ecology and evolution. Advances in Microbial Physiology, 57: 1−41. DOI: 10.1016/B978-0-12-381045-8.00001-1.
doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-381045-8.00001-1 |
|
|
Schloss PD , Westcott SL , Ryabin T , et al . , 2009. Introducing mothur: open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 75: 7537. DOI: 10.1128/AEM.01541-09.
doi: 10.1128/AEM.01541-09 |
|
|
Six J , Conant RT , Paul EA , et al . , 2002. Stabilization mechanisms of soil organic matter: implications for C-saturation of soils. Plant and Soil, 241: 155−176. DOI: 10.1023/A:10 16125726789.
doi: 10.1023/A:10 16125726789 |
|
|
Sommers LE, Nelson DW , 1972. Determination of total phosphorus in soils: A rapid perchloric acid digestion procedure. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 36: 902−904. DOI: 10.2136/sssaj1972.03615995003600060020x.
doi: 10.2136/sssaj1972.03615995003600060020x |
|
|
Ter Braak CJF, 1986. Canonical correspondence analysis: a new eigenvector technique for multivariate direct gradient analysis. Ecology, 67: 1167−1179. DOI: 10.2307/1938672.
doi: 10.2307/1938672 |
|
|
Tilman D , Downing JA , 1994. Biodiversity and stability in grasslands. Nature, 367: 363−365. DOI: 10.1038/367363a0.
doi: 10.1038/367363a0 |
|
|
Tu Q , Yu H , He ZL , et al . , 2014. GeoChip 4: a functional gene-array-based high-throughput environmental technology for microbial community analysis. Molecular Ecology Resources, 14(5): 914−928. DOI: 10.1111/1755-0998.12239.
doi: 10.1111/1755-0998.12239 |
|
|
Van der Heijden MGA , Klironomos J , Ursic M , et al . , 1998. Mycorrhizal fungal diversity determines plant biodiversity, ecosystem variability and productivity. Nature, 396: 69−72. DOI: 10.1038/23932.
doi: 10.1038/23932 |
|
|
Wang C , Wang X , Liu D , et al . , 2014. Aridity threshold in controlling ecosystem nitrogen cycling in arid and semi-arid grasslands. Nature Communications, 5: 4799. DOI: 10.10 38/ncomms5799.
doi: 10.10 38/ncomms5799 |
|
| Walkly A ,1934. An examination of the Degtjareff method for determining soil organic matter and a proposed modification to the chromic acid titration method. Soil Science, 37: 29−38. | |
| West NE , 1991. Nutrient cycling in soils of semiarid and arid regions. In: Skujins J (ed.). Semiarid Lands and Deserts, Soil Resource and Reclamation. Dekker Marcel, Inc, York New, pp. 295−332. | |
|
Yang CL , Sun TH , Zhou WX , et al . , 2007. Single and joint effects of pesticides and mercury on soil urease. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 19: 210−216. DOI: 10.1016/S10 01-0742(07)60034-5.
doi: 10.1016/S10 01-0742(07)60034-5 |
|
|
Zhalnina K , de Quadros PD , Camargo FA , et al . , 2012. Drivers of archaeal ammonia-oxidizing communities in soil. Frontiers in Microbiology, 3: 210. DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2012. 00210.
doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2012. 00210 |
|
|
Zhang LM , Hu HW , Shen JP , et al . , 2012. Ammonia-oxidizing archaea have more important role than ammonia-oxidizing bacteria in ammonia oxidation of strongly acidic soils. ISME Journal, 6(5): 1032−1045. DOI: 10.1038/ismej. 2011.168.
doi: 10.1038/ismej. 2011.168 |
| No related articles found! |
|
||