Article Information
- Wei Liu, ZongXing Li, Meng Zhu, Guo XiaoYan, Chen LiJuan . 2016.
- Temperature and precipitation changes in Extensive Hexi Region, China, 1960-2011
- Sciences in Cold and Arid Regions, 8(3): 0212-0226
- http://dx.doi.org/10.3724/sp.j.1226.2016.00212
Article History
- Received: November 03, 2016
- Accepted: May 10, 2016
2. University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
Global climate change has been evident in many places worldwide for quite some time (Peterson et al., 2002; Zhang et al., 2005; New et al., 2006; Aguilar et al., 2009). Variations and trends in extreme climate events can be more sensitive to climate change than the mean values, and thus the extreme events have received much attention (Easterling et al., 2000). Alexander et al.(2006)analyzed global changes in daily climate extremes and concluded that significant warming throughout the 20th century and temperature differences were particularly pronounced in the most recent two decades. Temperature and precipitation extremes have also been studied in many regions of the world (Aguilar et al., 2005; Haylock et al., 2006; Klein et al., 2006; You et al., 2011; Li et al., 2012a, 2012b). These studies have shown that significant widespread changes in temperature extremes are associated with warming, whereas changes in precipitation extremes exhibit much lower spatial coherence than those in temperature extremes.
Annual mean temperature increased by 0.4-0.5 ℃ from 1860 to 2005 in China (China Meteorological Administration, 2006). On the whole, the increasing trend is more remarkable in western China, particularly in the northwest (Ye et al., 2004; Liu et al., 2005). With temperature and precipitation rising, regional climate is experiencing a change from warm-dry to warm-wet in northwestern China (Shi et al., 2002; Shi, 2003). Under climate warming, mass loss from mountain glaciers and ice-caps was 1.55×1011 t/a (water equivalent) during 1960/1961-2003/2004(IPCC, 2007). Glaciers in China have been retreating since the early 20th century, and the retreat has intensified since the 1980s (Pu et al., 2004). Considerable research by Chinese glaciologists has shown that glaciers in western China are sensitive to climate change (Shi, 2001; Yao et al., 2004; Li et al., 2011, 2015a, 2015b; Wang et al., 2011a, 2011b, 2012).
Based on the research by Wang et al.(2016), annual temperature has exhibited a fluctuating increase in the past 50 years in the upper Heihe River basin, and accretive warming since the 1990s, particularly in winter when the greatest warming occurred. Zhang and Guo (2002)confirmed that the eastern Qilian Mountains showed obvious warming in the 1990s, while other regions already had by the mid-1980s. Yin et al.(2009)found that the annual mean temperature growth accelerated after the mid-1980s, and the warming magnitudes in winter were larger than in summer, and also greater at night than during the day. The temperature of the Hexi Corridor showed a rising trend from 1950 to 1999, and the precipitation in the middle and west regions increased distinctly (Cheng et al., 2015). The temperature of the upper region of the Heihe River has been increasing since the 1950s, particularly in autumn and winter, and similarly for precipitation, mainly summer precipitation (Feng et al., 2016). The total runoff value of the upper Heihe River showed an increasing trend in the last half of the century, resulting from an increase in summer precipitation, as well as an increase of melting water from glaciers and snow, which led to a runoff increase in the flood season (Ding et al., 2000; Li et al., 2006). In terms of the climate change in the Qilian Mountains, Tang (1985) reported a third-degree polynomial relationship of precipitation with altitude in the Qilian Mountains. He also showed that temperature increased significantly after the mid-1980s in the Qilian Mountains, mainly related to the rise of temperature in autumn and winter. The same author reported that precipitation experienced an increasing trend from the 1960s to the 1980s, and a decreasing trend in the 1990s. According to Jia et al.(2008a), the precipitation trend was on the increase again after 2000. Chen et al.(2007)studied the regional differences in precipitation patterns in the eastern and western Qilian Mountains. Zhang et al.(2007)suggested that water vapor was mainly brought on by the westerly winds in the northwestern Qilian Mountains, by the South Asia monsoon in the middle-south Qilian Mountains, and by East Asia monsoon in the northeastern Qilian Mountains.
The Extensive Hexi region is a transition zone between the monsoon and the westerlies, and includes three inland river basins and two deserts. It is important because of its climatic sensitivity and ecological fragility. The ecological environment in this region has encountered serious degradation due to global climate changes and human activities (Zhang Feng et al., 2015). The surface runoff is closely related to the climate change, and the variation in runoffaffects the socio-economic development and ecosystems restoration in this region. Although past climate research has mainly concentrated on the variation of average temperature and precipitation in the Qilian Mountains or the Hexi Corridor over the study region, it still lacks a comprehensive understanding of climate change in the whole region, and there has been essentially no research on the variation of climate extremes. For this reason, we selected the Extensive Hexi region as the study area and investigated its changes in both climate averages and extremes.
The objectives of this study were to investigate the changes in temperature and precipitation during 1960-2011 and to assess their relationship with altitude. An additional motivation behind the study was to improve understanding of the frequency, intensity, and duration of climate variabilities which strongly impact inland river runoffs. These results can stimulate sensible utilization of water resources and, for example, development of the Hexi Oasis.
2 Materials and methods 2.1 Study areaThe Extensive Hexi Region (36°N-43°N, 92°E-107°E), with an area of 31.55×104 km2, lies in northwestern China and includes three inland river basins, the Shiyanghe River Basin, the Heihe River Basin, and the Shulehe River Basin, and two deserts, the Badain Jaran Desert and the Tengger Desert. This region, which includes the Hexi Corridor, also includes the Qilian Mountains, which lie in the northeastern edge of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau of China. These mountains consist of several parallel mountains and valleys, stretching 850 km in length from the northwest to the southeast, and extending 200-300 km in width from south to north. The altitudes of about 30% of the peaks in the Qilian Mountains are above 4, 000 m, and the highest peak is Tuanjie Peak with an altitude of 5, 826.8 m. There are 2, 859 glaciers in the Qilian Mountains, with a total area of 1, 972.5 km2, and the total volume of the glaciers are 84.48 km3(Sun, 2015). The temperature varies with altitude. The annual precipitation, which decreases from east to west and from south to north, varies from 400 to 700 mm. The Qilian Mountains are very important to the Hexi Oasis because they provide the sources of Shiyanghe, Heihe, and Shulehe rivers coming from precipitation and snow and glacier meltwater. The Hexi Corridor is located at the western end of the Wushaoling Mountains and includes five cities. The corridor covers an area of 271, 100 km2 and crosses an arid to semiarid part of China, with mean annual precipitation of 50-200 mm, with precipitation decreasing from east to west. Annual potential evaporation increases from more than 2, 000 mm in the east to 3, 500 mm in the west. The five main cities in the Hexi Corridor are situated within inland watersheds with an annual mean runoff that totals 1.6 km3 in the Shiyanghe Watershed, 3.2 km3 in the Heihe Watershed, and 1.72 km3 in the Shulehe Watershed.
The Badain Jaran Desert (39°N-41°N, 100°E -104°E) spans approximately 50, 000 km2 within the Alashan Plateau and is considered to be the fourth largest desert in China (Figure 1). It is bordered by mountains and ranges to the south and southeast (the Heishantou and Yabulai Mountains, respectively), and the lowland areas of the Gurinai Grassland and the Guezi Hu Lacustrine Plains to the west and north. The landscape consists primarily of unconsolidated sand dunes. Climatically, the area is strongly continental and is regarded as a cold desert. Daily daytime temperatures in summer months reach 40 ℃, and mean monthly temperatures fall to −10 ℃ in January while sub-zero minimum temperatures prevail for most of the year. The southeastern Badain Jaran is near the current northern extent of the East Asian monsoon and provides the primary source of precipitation, 70% of which falls from July to September. Cold and dry continental air masses from prevailing westerly winds dominate in winter. The Tengger Desert is located in the arid-semiarid area of northwestern China, with a total area of 36, 000 km2. The desert is bounded by the Qilian Mountains in the southwest and by the Yabulai Mountains in the northwest. The Helan Mountains, a barrier for the East Asian monsoon, separates the Tengger Desert from the Mu Us Sandy Land to the east. To the south, the desert stretches as far as the Loess Plateau. Climatically, the area is situated at the conjunction of the arid and hyper-arid northwest, the arid-semiarid southeast, and the cold-high mountain-plateau regions in the southwest. The mean annual temperature and precipitation are 7.8 ℃ and 115 mm, respectively, while the mean annual potential evaporation is about 2, 600 mm. The Tengger Desert is primarily covered with mobile sand dunes.
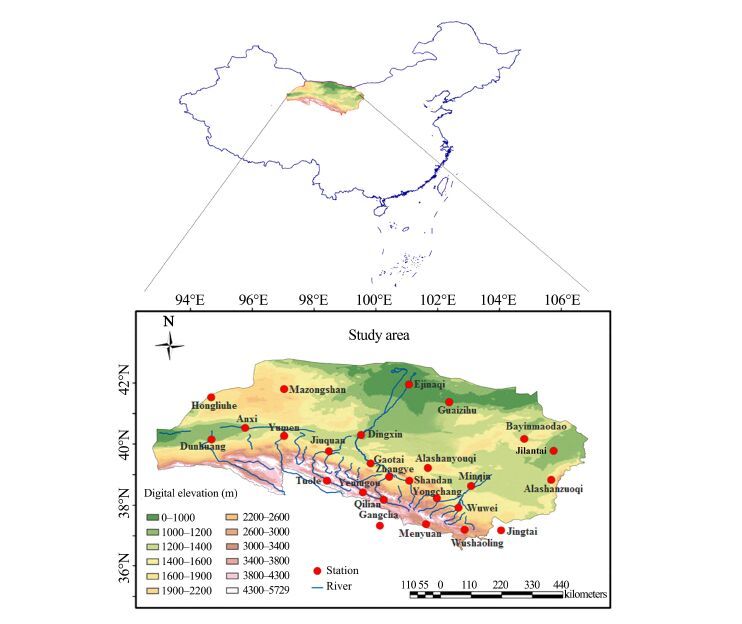
|
| Figure 1 Study area and the selected weather stations |
The daily precipitation, maximum temperature, and minimum temperature data used in this study were provided by the National Climate Center, China Meteorological Administration (CMA)(http:// www.nmic.gov.cn). Along with a rapid development of meteorological observations, the nationwide network of weather stations in China began operating in the 1950s. There are 36 stations in the original data set that have maintained daily observations since the 1950s or 1960s. We selected 26 stations (Figure 1) from the dataset based on the quality-control and homogenization procedures described in Li et al.(2011). After data-quality control and homogeneity assessment, RClimDex was used to calculate climate indices from the daily data. The Expert Team for Climate Change Detection and Indices (ETCCDI; http://cccma. seos.uvic.ca/ETCCDI/software.shtml) has been coordinating a suite of 11 precipitation and 16 temperature indices adopted by the IPCC Fourth Assessment Report (AR4). Indices not relevant to the studied region were omitted, leading to a final selection of 12 temperature indices and 10 precipitation indices (Table 1). These were determined for the quality-controlled data from
| Index | Descriptivename | Definition | Units |
| TXx | Warmest-day temperature | Annual highest TX | ℃ |
| TNx | Warmest-night temperature | Annual highest TN | ℃ |
| TXn | Coldest-day temperature | Annual lowest TX | ℃ |
| TNn | Coldest-night temperature | Annual lowest TN | ℃ |
| TN10 | Cold-night frequency | Percentage of days when TN<10th percentile of 1961-1990 | d |
| TX10 | Cold-day frequency | Percentage of days when TX<10th percentile of 1961-1990 | d |
| TN90 | Warm-night frequency | Percentage of nights when TN>;90th percentile of 1961-1990 | d |
| TX90 | Warm-day frequency | Percentage of days when TX>;90th percentile of 1961-1990 | d |
| DTR | Diurnal-temperature range | Annual mean difference between TX and TN | ℃ |
| ID | Ice days | Annual count when TX (daily maximum)<0℃) | d |
| FD | Frost days | Annual count when TN (daily minimum)<0℃ | d |
| GSL | Growing-season length | Annual count between first span of atleast 6 days with TG>5℃ After winter and first span after summer of 6 days with TG>5℃ | d |
| PRCPTOT | Wet-day precipitation | Annual total precipitation from wet days | mm |
| SDⅡ | Simple daily intensity index | Average precipitation on wet days | mm/d |
| CDD | Consecutive dry days | Maximum number of consecutive dry days | d |
| CWD | Consecutive wet days | Maximum number of consecutive wet days | d |
| R10mm | Number of heavy precipitation days | Annual count of days when RR≥10mm | d |
| R20mm | Number of heavier precipitation days | Annual count of days when RR≥20mm | d |
| R95 | Very wet day precipitation | Annual total precipitation when RR>;95th percentile of 1961-1990 daily precipitation | mm |
| R99 | Extremely wet day precipitation | Annual total precipitation when RR>;99th percentile of 1961-1990 daily precipitation | mm |
| RX1day | Maximum1-day precipitation | Annual maximum1-day precipitation | mm |
| RX5day | Maximum 5-day precipitation | Annual maximum consecutive 5-day precipitation | mm |
| * All indices are calculated by RClimDex (RClimDex is a Microsoft Excel-based program that provides an easy-to-use software package for the calculation of indices of climate extremes for monitoring and detecting climate change). Abbreviations are as follows: TX, daily maximum temperature; TN, daily minimum temperature; TG, daily mean temperature; RR, daily precipitation. A wet day is defined when RR ≥ 1 mm, and a dry day when RR< 1 mm. Indices are included for completeness but some are not analyzed further in this paper. | |||
A regionally averaged anomaly series for climate series was calculated as follows:
where xr, t is the annual regionally averaged value of the climate series (such as precipitation) at year t, xi, t is the value for station i at year t, Xi is the 1961-2008 mean value at station i, and nt is the number of stations with data in year t. To avoid the average series being dominated by those stations with a high value, xi, t was standardized by dividing them by the station-specific standard deviation. The regional climate series were converted into trends per decade, and a linear trend was considered to be statistically credible if it was significant at the 0.05 confidence level. The number of stations with the same trend as that for the whole region was counted for each series, and stations with significant trends were also identified. In addition, the nine-year smoothing average was used to show the inter-decadal variation of climatic series.
3 Results and discussion 3.1 Average temperature and precipitationThe annual average temperature was 5.88 ℃ in the Extensive Hexi Region during 1960-2011, at a statistically significant warming rate of 0.34 ℃/10a. The warming rate was much higher than that of the whole country, and supported previous findings that the increasing trend is more remarkable in western China, particularly in the northwest (Ye et al., 2004; Liu et al., 2005). Initially, the inter-annual variation slowly decreased during 1960-1975 and subsequently increased (Figure 2). The annual average maximum and minimum temperatures were 13.68 and −0.82 ℃, which increased by 0.28 and 0.42 ℃/10a, respectively. The maximum temperature had inter-annual variation similar to the average temperature, but the minimum temperature exhibited a particularly significant warming trend during 1960-2011. In addition, the warming has accelerated since the mid-1980s over the study region, and the regional trends of average, maximum, and minimum temperature were −0.01, −0.10, and 0.14 ℃/10a, respectively, in 1960-1985, whereas they were 0.43, 0.36, and 0.55 ℃/10a during 1986-2011; the average values in the later period were 1.00, 0.85, and 1.17 ℃ higher than in the former period (Figure 2). This result coincided with previous studies which indicated that the annual mean temperature growth accelerated after the mid-1980s in the Qilian Mountains (Jia et al., 2008b; Yin et al., 2009).
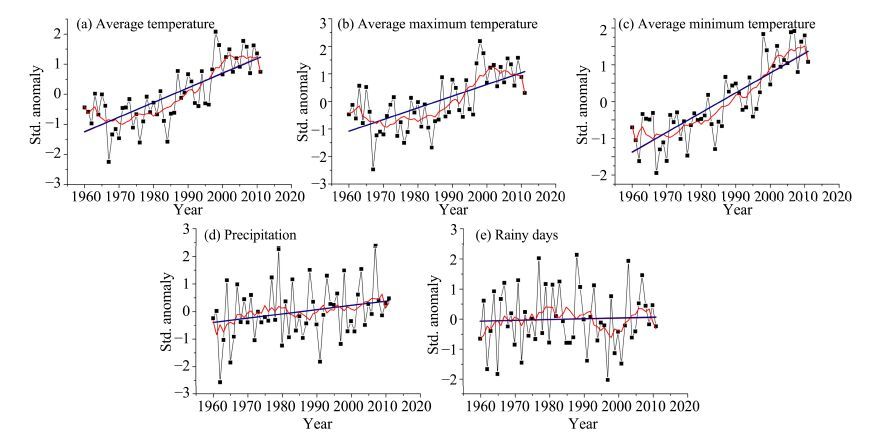
|
| Figure 2 Inter-annual variation of average, maximum, and minimum temperature, precipitation, and number of rainy days in the Extensive Hexi Region |
Precipitation exhibited a slow increase during the studied period, with an average value of 175 mm and an insignificant regional trend of 3.78 mm/10a. Rainy days slowly increased during 1960-1980, slowly decreased in the following period of 1981-2000, and then increased again in 2001-2011, with an average value of 58 days; then during the entire period there was an insignificant growth rate of 0.16 d/10a.
In terms of spatial patterns, the warming magnitudes expressed by average temperature were relatively lower in the central western Hexi Corridor and the northern Tengger Desert, and were relatively higher in the downstream areas of the Shulehe River and the Heihe River, and in the Badain Jaran Desert and the Shiyanghe River Basin. All stations recorded statistically significant temperature warming (Figure 3). The maximum temperatures increased in the western study area and also from the inner area to the periphery of the Badain Jaran Desert, but there was less warming in the Heihe River Basin, the Shiyanghe River Basin, and the Shulehe River Basin. As to regional differences, the warming expressed by elevated maximum temperatures mainly occurred in the west, whereas the minimum temperature was typical for the east. Except for four stations in the downstream areas, all other stations recorded precipitation increases, although the increases from only four stations were significant. Increased precipitation mainly occurred in the Qilian Mountains and the Hexi Corridor, whereas the other regions exhibited decreasing trends during 1960-2011, particularly the Badain Jaran Desert and the downstream area of the Shulehe and Heihe River basins.
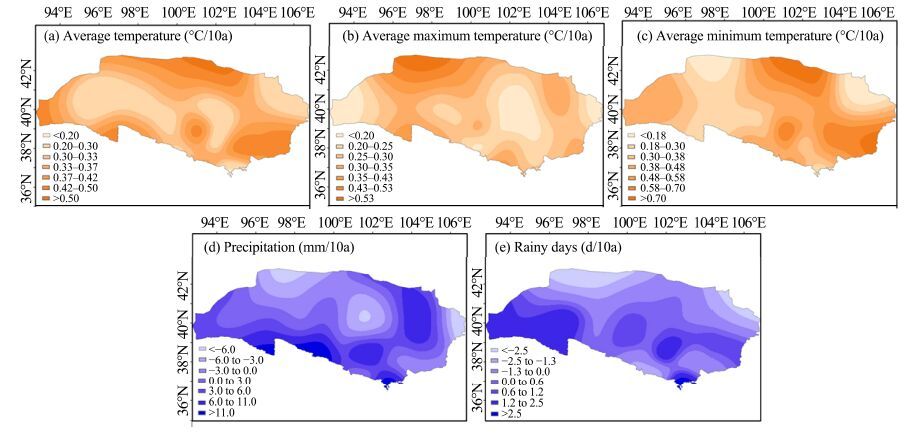
|
| Figure 3 Spatial patterns for average, maximum, and minimum temperature, precipitation, and number of rainy days in the Extensive Hexi Region |
The number of rainy days decreased at eight stations during 1960-2011. They increased mainly in the Qilian Mountains and the Hexi Corridor, with the western area generally seeing larger magnitudes. In contrast, the number of rainy days decreased mainly in the deserts and the downstream areas of the three inland river basins.
3.2 Temperature and precipitation extremes 3.2.1 Temperature extremesRegional time series for cold-day frequency (TX10), cold-night frequency (TN10), coldest-day temperature (TXn), coldest-night temperature (TNn), ice days (ID), and frost days (FD) displayed trends consistent with warming (Figure 4). However, those for TNn and TXn were not significant, as shown in Table 2. TX10 and TN10 decreased during 1960-2011 at all stations, with 20 and 24 stations showing significant decreases, respectively. The lower decrease for TX10 was mainly observed in the Hexi Corridor and Badain Jaran Desert, whereas the larger decrease mainly occurred in the Qilian Mountains and in the downstream areas of the three inland rivers, which reflected more warming mainly in the higher-altitude regions and desert areas (Figure 5). In the western study region and the northern Tengger Desert, TN10 decreased less than in the Shiyanghe River Basin, Heihe River Basin, and Badain Jaran Desert. There was an increase in TX10 in the mid-1960s, followed by a decrease until 2000 and then by another increase in 2001-2011, yielding an overall warming trend for TN10 during 1960-2011. In addition, the regional trends for TN10 were lower than for TX10(Table 2). These characteristics indicate that increasing temperatures are more pronounced at night than in the day. Similar results were obtained by Yin et al.(2009), who found that the warming magnitudes in the Qilian Mountains were greater at night than during the day.
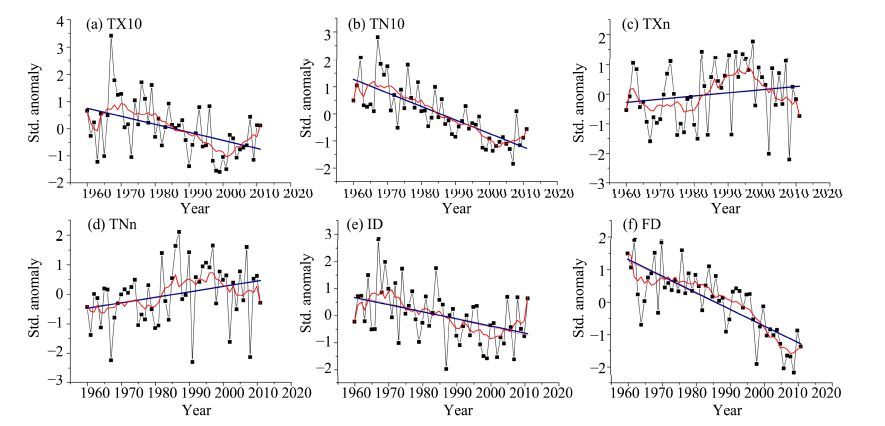
|
| Figure 4 Inter-annual variation for cold extremes of the Extensive Hexi Region |
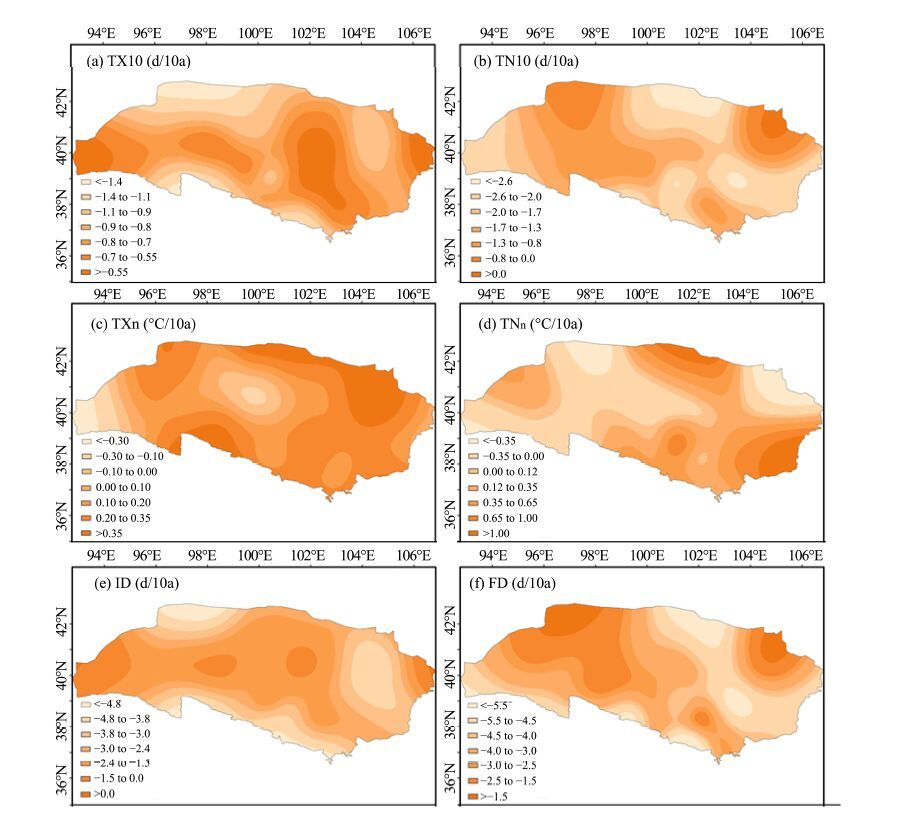
|
| Figure 5 Spatial patterns for cold extremes of the Extensive Hexi Region |
| Parameter | Trends (days/10a) | R | Averagevalue (days) |
| DTR | −0.15 | −0.62 | 14.50 |
| FD (days/10a) | −3.69 | −0.77 | 184.29 |
| GSL (days/10a) | 3.15 | 0.55 | 201.73 |
| ID (days/10a) | −2.85 | −0.45 | 57.72 |
| TN10(days/10a) | −1.69 | −0.76 | 8.61 |
| TN90(days/10a) | 2.72 | 0.79 | 13.41 |
| TNn (℃/10a) | 0.31 | 0.26 | −25.10 |
| TNx (℃/10a) | 0.37 | 0.54 | 19.42 |
| TX10(days/10a) | −0.82 | −0.45 | 9.48 |
| TX90(days/10a) | 1.69 | 0.62 | 12.63 |
| TXn (℃/10a) | 0.23 | 0.17 | −11.93 |
| TXx (℃/10a) | 0.28 | 0.37 | 33.58 |
| Values for trends significant at the 5% level are set in bold. Refer to Table 1 for descriptions of parameters. | |||
Similar to TX10 and TN10, the coldest-day temperature (TXn) and coldest-night temperature (TNn) also indicated warming, but the regional trends were not significant at the 0.05 confidence level (Table 2). TXn slowly decreased from 1960 to 1980, increased until 2000, and again decreased after 2001, while TNn kept increasing until 2000 and then decreased during 2001-2011(Figure 4). Increasing trends for TXn and TNn were recorded at 24 and 22 stations, respectively, and only seven stations showed significant warming, mainly distributed in the Heihe River Basin. The greater TXn warming mainly occurred in the Qilian Mountains and desert areas, and the warming magnitudes were also greater in the east than in the west. Except for the northeastern Tengger Desert, the middle Hexi Corridor, and the Shulehe River Basin, TNn displayed larger warming in other study regions (Figure 5).
All stations showed a significant decreasing trend for FD, while ID decreased at only 18 stations, mainly located in the eastern and middle Qilian Mountains, the Hexi Corridor, and the Tengger Desert. Frost days generally decreased through the analysis period and indicated evident warming (Figure 4), at a significant regional trend of −3.69 days/10a (Table 2). Except for the western Hexi Corridor, the Mazong Mountains, and the northern Tengger Desert, FD in the other regions decreased more significantly, especially in the Qilian Mountains, Shiyanghe River Basin, and Heihe River Basin. ID increased in the 1960s and then decreased during 1971-2000 and again increased after 2001(Figure 4), at a significant regional rate of −2.85 days/10a (Table 2). ID decreased more in the Qilian Mountains, Tengger Desert, and Mazong Mountains, but with relatively lower magnitudes in the middle-stream of the Heihe River and the Shulehe River basins (Figure 5).
Historical diurnal temperature ranges (DTR) showed increasing trends because of the rapid increases in the minimum temperatures in recent decades (Liu et al., 2009). The present study also indicated a warming trend of DTR in the Extensive Hexi Region (Figure 6). Approximately 22 stations recorded decreasing trends; these were statistically significant at 17 stations, mainly distributed at the east and middle of the study region. As shown in Figure 7, a lower increasing trend occurred in the northern Tengger Desert, the eastern Shulehe River Basin, and the Mazong Mountains. Stations with decreases in DTR were mainly located in the Shiyanghe River Basin, Heihe River Basin, Badain Jaran Desert, and the westernmost part of the study area (Figure 7).
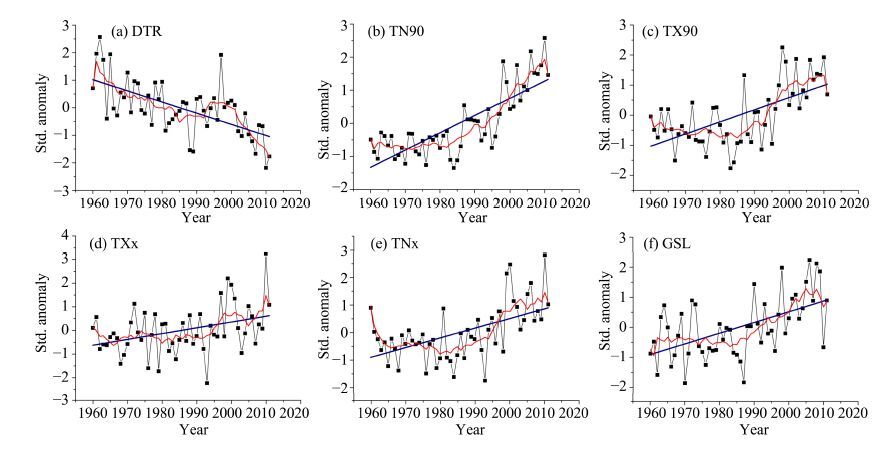
|
| Figure 6 Inter-annual variation for warm extremes in the Extensive Hexi Region |
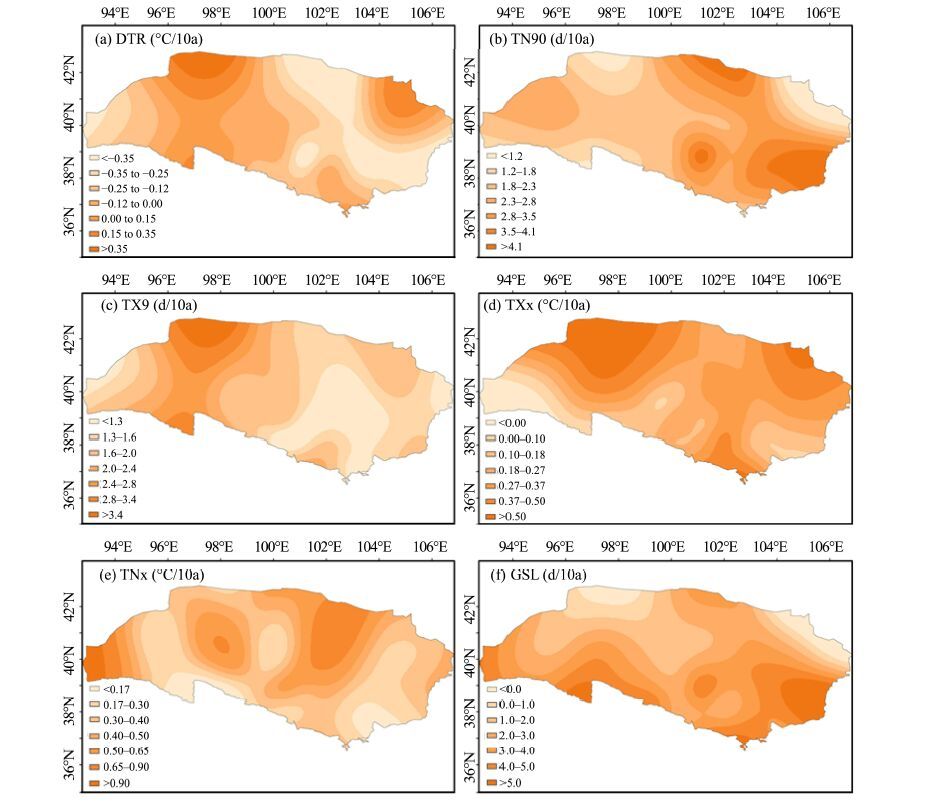
|
| Figure 7 Spatial patterns for warm extremes in the Extensive Hexi Region |
Warm extremes were assessed by looking at regional averages of warm-night frequency (TN90), warm-day frequency (TX90), warmest-day temperature (TXx), warmest-night temperature (TNx), and growing-season length (GSL; Table 2). The trends displayed by these parameters were consistent with significant warming during 1960-2011(Figure 6). Moreover, these parameters also showed the larger warming magnitudes with significance during 1986-2011 than in the period of 1960-1985(Table 3), which also supported the results that the warming has accelerated since the mid-1980s over the study region (Figure 2, Yin et al., 2009). It seems clear that the warming magnitudes shown by TN90 were greater than those shown by TX90, as all the stations displayed a significantly increasing trend for these two indices (Table 2). TN90 increased with the larger warming magnitudes in the eastern region to the boundary of the Heihe River, whereas TX90 displayed larger warming in the western study area, which also reflected the regional differences in climate warming (Figure 7).
| Period | DTR | FD | GSL | ID | TN10 | TN90 | TNn | TNx | TX10 | TX90 | TXn | TXx |
| 1960-1985 | −0.25 | −1.22 | −0.10 | −1.10 | −1.32 | −0.34 | 0.32 | −0.32 | 0.02 | −1.13 | −0.13 | −0.12 |
| 1986-2011 | −0.19 | −6.16 | 6.59 | 0.47 | −1.31 | 4.93 | −0.64 | 0.86 | −0.32 | 3.32 | −1.11 | 0.59 |
As shown in Figure 6, the warming magnitudes were also higher as expressed by TNx at a rate of 0.37 ℃/10a (Table 2). Twenty stations had significant increasing trends in TNx, compared with only 10 stations in the case of TXx. TNx slowly decreased before 1980 and then clearly increased during 1981-2011, while TXx remained constant before 1990 and then increased (Figure 6). Consequently, it can be concluded that the greater warming of both cold extremes and warm extremes mainly occurred at night rather than during the day. TNx indicated the highest warming in the Badain Jaran Desert, with the warming magnitudes decreasing from inner to outer areas (Figure 7). Near the Mazong Mountains and the northern Tengger Desert, the warming magnitudes related to TXx decreased from north to south, while the Qilian Mountains had the relatively largest warming magnitudes (Figure 7).
Consistent with previous studies, the GSL also significantly increased over the study region (Figure 6). All the stations displayed an increasing trend in GSL, and it was statistically significant at about 20 stations. As the warming magnitudes decreased from south to north, with particularly high warming in the Qilian Mountains and the Shiyanghe River Basin, it seems that climate warming was more pronounced at higher-altitude regions (Figure 7).
In summary, temperature extremes were associated with evident warming in the studied region during 1960-2011. The greatest warming occurred mainly in high-altitude areas and desert areas. Warming associated with elevated low- and high-temperature extremes was greater during the night than in the day.
3.3.2 Precipitation extremesSimilar to temperature extremes, the intensity significance of changes in precipitation extremes during 1960-2011 was also high, with only the maximum 5-day precipitation (RX5day), the average precipitation on wet days (SDⅡ), and consecutive wet days (CWD) characterized by non-statistically significant trends (Table 4). The wet-day precipitation (PRCPTOT) had a continuing and significant increasing trend of 11.57 mm/10a (Figure 8). Twenty-three stations displayed increasing trends, with 13 of them, located at the east of Qilian Mountains and Hexi Corridor, being significant. Geographically, the magnitudes of wet-day precipitation declined from the Qilian Mountains to the desert areas. It is apparent that a precipitation increase mainly occurred in higher-altitude areas (Figure 9). Similar results were obtained by Jia et al.(2008b), who found that the increase of precipitation in the Qilian Mountains was greater than in the Hexi Corridor. The average precipitation on wet days (SDⅡ) had a weak decreasing trend with fluctuation (Figure 8), and increased in 1960-1975, decreased during 1975-1985, and then had a fluctuating increase, with 15 stations exhibiting a decreasing trend. Areas with increasing precipitation were mainly in the northern regions, especially the Badain Jaran and Tengger Deserts, whereas the decreasing trends mainly occurred in the Hexi Corridor and the Qilian Mountains (Figure 9).
| 1960-2011 | Trends (days/10a) | R | Averagevalue (day) |
| CDD (days/10a) | −26.15 | −0.80 | 161.42 |
| CWD (days/10a) | 0.02 | 0.10 | 3.49 |
| PRCP (mm/10a) | 11.57 | 0.67 | 154.60 |
| R10(days/10a) | 0.31 | 0.57 | 3.99 |
| R20(days/10a) | 0.06 | 0.33 | 0.76 |
| R25(days/10a) | 0.03 | 0.32 | 0.36 |
| R95(mm/10a) | 3.12 | 0.48 | 32.78 |
| R99(mm/10a) | 0.99 | 0.33 | 9.78 |
| RX1(mm/10a) | 0.66 | 0.36 | 19.67 |
| RX5(mm/10a) | 1.00 | 0.28 | 30.67 |
| SDⅡ (mm/day/10a) | −0.03 | 0.10 | 4.92 |
| Values for trends significant at the 5% level are set in bold. Refer to Table 1 for descriptions of parameters. | |||
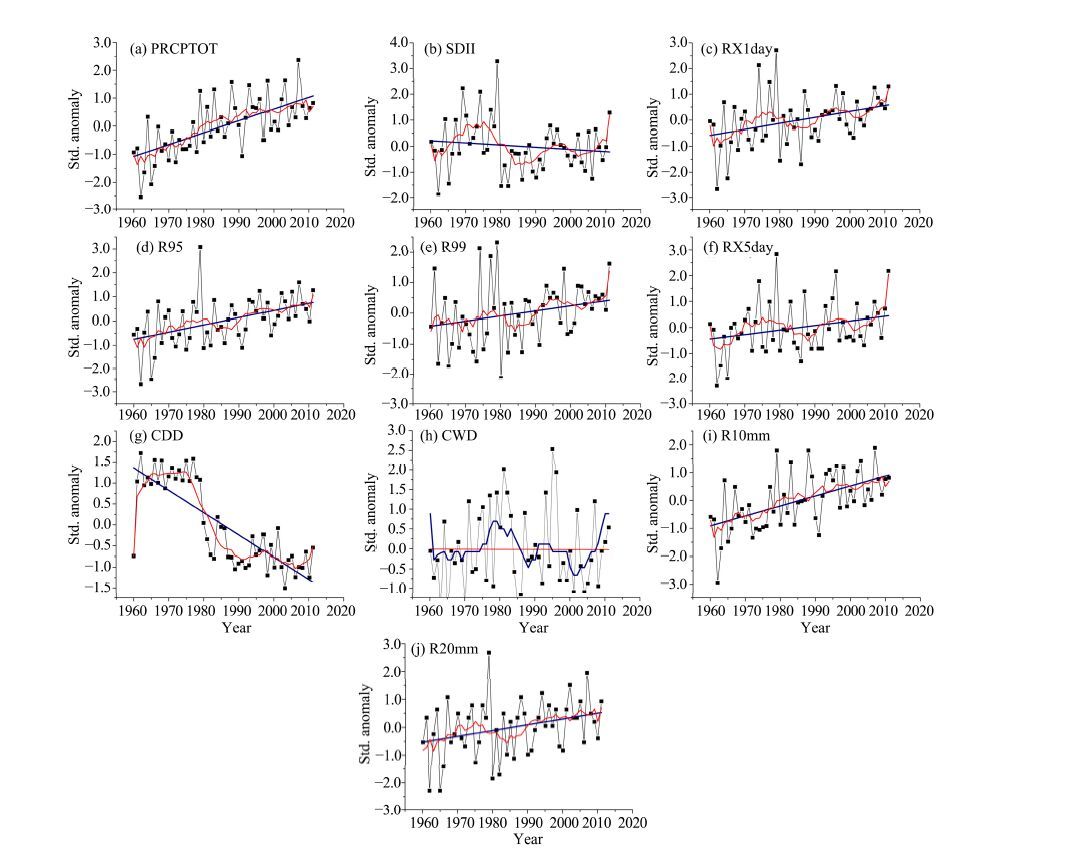
|
| Figure 8 Inter-annual variation for precipitation extremes in the Extensive Hexi Region |
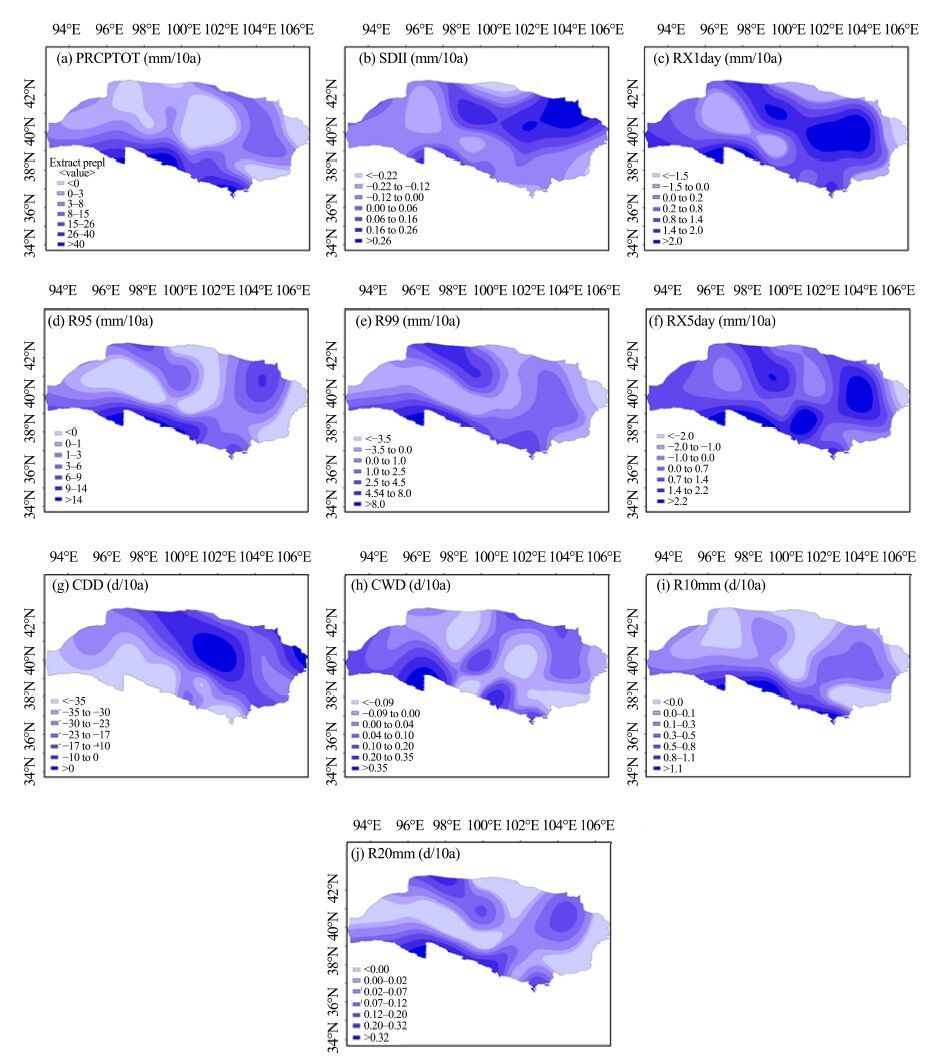
|
| Figure 9 Spatial patterns for precipitation extremes in the Extensive Hexi Region |
On the whole, the increase of very (R95) and extreme wet-day precipitation (R99) was common in the study region (Figure 8). Furthermore, the increase in these two indices was significant (Table 4), pointing to an increase in extreme precipitation events. There was an increasing trend at 17 and 19 stations for R95 and R99, respectively, located on the upstream and middle areas of the Heihe River Basin and Shiyanghe River Basin, but the trends were significant at only four and two stations, respectively. The rising trends declined spatially from north to south. The middle and western Hexi Corridor, the downstream areas of the Heihe River Basin, and the northeastern Tengger Desert showed decreasing trends. The precipitation strength increased mainly in higher-altitude regions (Figure 9).
The maximum 1-day precipitation (RX1day) and the maximum 5-day precipitation (RX5day) clearly increased with fluctuation, but only the regional trends for RX1day were significant (Figure 8). Twenty stations had increasing trends for these two indices, but the trends were significant at only six and four stations for RX1day and RX5day, respectively. The RX1 variation declined from the interior to the periphery of the Badain Jaran Desert, particularly in the middle and western Hexi Corridor, whereas it increased in the desert areas (Figure 9). RX5day increased mainly in the Shiyanghe River Basin and the middle and eastern Qilian Mountains, while RX5day declined in the western study region (Figure 9). Statistically significant increases of the maximum 1-day and 5-day precipitation suggest an overall increase in precipitation strength in the studied region (Figure 8).
All 26 stations had decreases in consecutive dry days (CDD), and this was significant at 24 stations (Table 4), mainly distributed in the Qilian Mountains and the Hexi Corridor, which saw an increase in rainy days. The significant decrease of CDD was shown most by stations in the Qilian Mountains, and indicated a precipitation increase in those areas. In the Badain Jaran Desert, CDD decreased from the interior to the periphery, with larger decreases in the Qilian Mountains, Hexi Corridor, and Shulehe River Basin. CDD increased in the desert areas (Figure 9).
Consecutive wet days (CWD) slowly increased in 1960-1980, then decreased during 1981-2000, and increased again after 2001(Figure 8). Approximately 18 stations showed an increasing trend during 1960-2011, and these stations were mainly distributed in the Qilian Mountains and Hexi Corridor. As shown in Figure 9, the greater increase was mainly in the Shulehe River Basin, whereas it decreased in the Mazong Mountains, Badain Jaran Desert, and the downstream area of the Shiyanghe River Basin. These characteristics also confirmed the decrease in rainy days in desert areas during 1960-2011.
The number of heavy precipitation days (R10 mm) had a significant increasing trend (Figure 8) in five stations, and 21 stations experienced a decrease, being significant at only seven stations distributed in the Qilian Mountains at 0.31 day/10a (Table 3). The increasing magnitudes declined spatially from the Qilian Mountains to the desert areas, particularly in the Mazong Mountains, Badain Jaran Desert, and Tengger Desert (Figure 9). The number of heavier precipitation days (R20 mm) also had a significant increasing trend with fluctuation (Figure 8). About 20 stations had increasing trends of R20 mm, but this was significant at only three stations, located in the Heihe River Basin. Except for the middle and western Hexi Corridor, the northern Badain Jaran Desert, and the eastern Tengger Desert, other regions displayed an increasing trend, particularly at higher altitude regions (Figure 9). These variations again indicated an increase in precipitation and rainy days mainly in higher-altitude regions, whereas the precipitation strength also increased in desert areas.
The contribution from extreme precipitation to total precipitation increased significantly between 1960 and 2011, as shown in Figure 10. Precipitation of very wet days (R95) accounted for an average of 19% of the total precipitation, with a rate of 1.4%/10a (ranging from 6% to 28%). The average contribution of extremely wet days’ precipitation was 6%(ranging from 0 to 11%), and the regional trend (0.4%/10a) was not significant. These characteristics also reflect the contribution of an increase in precipitation extremes to the total precipitation in the studied region. Liu et al.(2005) reported that 95% of the total increase of precipitation in China during 1960-2000 was due to increased frequency of heavy precipitation events.
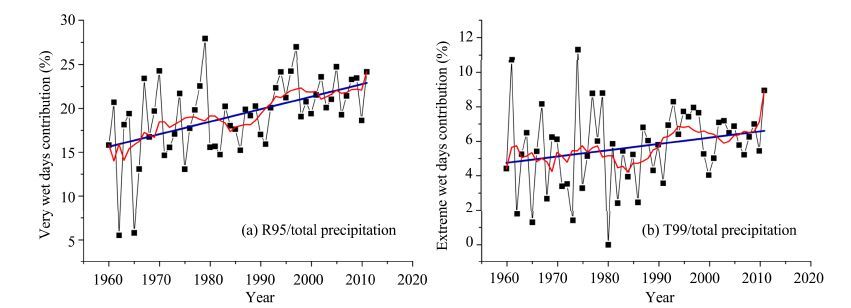
|
| Figure 10 Contribution for R95 and R99 to total precipitation during 1960-2011 in the Extensive Hexi Region |
Significant correlations with altitude (942-3, 368 m) were found for diurnal temperature range (DTR), frost days (FD), ice days (ID), and cold-day frequency (TX10). In contrast, no significant correlations with altitude were observed for the magnitudes of the trends of annual mean temperature, maximum temperature, and minimum temperature (Table 5). The increasing spatial trend of these indices with altitude was clear. Only regional trends of growing season length (GSL) and coldest day (TXn) displayed a statistically significant positive correlation with altitude, but warm-night frequency (TN90), coldest night (TNn) and warmest night (TNx), warm-day frequency (TX90), and warmest day (TXx) showed a non-significant relationship with altitude (Table 5). Overall, several significant decreases in temperature indices with altitude in the study region were relatively apparent for the period 1960-2011, and altitude dependence of the cold extremes (TX10, FD, ID, and TXn) was greater than that of the warm extremes (only GSL). These characteristics indicate more warming at higher-altitude regions, especially temperature extremes.
| ID | FD | GSL | TXn | TNx | TX10 | |
| Elevation (m) | 0.73 | 0.37 | 0.40 | 0.43 | 0.30 | 0.64 |
| Refer to Table 1 for descriptions of parameters. | ||||||
The significant positive correlations between altitude and the precipitation trends reflected precipitation increases in the higher-altitude regions (Table 6). The positive correlation between altitude and the trend of CDD was also significant at the 0.05 level. The regional trend of wet-day precipitation (PRCPTOT) and number of heavy precipitation days (R10 mm) and number of heavier precipitation days (R20 mm) displayed a statistically positive correlation with altitude, showing that the trend of increasing precipitation and rainy days with altitude was strong, whereas the trend of average precipitation on wet days (SDⅡ) was not significant. Thus, it can be deduced that the increasing precipitation strength mainly occurred at higher altitudes (e.g., 2, 788-3, 368 m). R95, R99, Rx1day, and Rx5day also displayed significant increases with increasing altitude, which indicated that the increase of extreme precipitation events also occurred in higher-altitude regions. Overall in the study region during 1960-2011, the trends of almost all the precipitation indices (with the exception of CWD and SDⅡ) significantly increased with altitude. Compared with temperature extremes, the significance of changes in precipitation extremes with altitude during 1960-2011 was high. One reason is that the Qilian Mountains can be influenced by monsoonal circulations, and another reason is the influence from the extremely dry underlying surfaces in other regions, which are mainly covered by deserts with rapid heat absorption and dissipation.
| Precipitation | RX1day | RX5day | R10mm | R20mm | CDD | R95 | R99 | PRCPTOT | |
| Elevation (m) | 0.63 | 0.33 | 0.43 | 0.93 | 0.75 | 0.56 | 0.77 | 0.75 | 0.93 |
| Refer to Table 1 for descriptions of parameters. | |||||||||
Fifty years of meteorological data from 26 stations in the Hexi Region of China were used to assess the change in average temperature and precipitation, and their extremes. During 1960-2011 the annual average, maximum, and minimum temperatures were on a significant warming trend. The temperature increases were statistically significant at all the observation sites, although the warming magnitudes of average temperatures were relatively larger in higher-altitude (mountainous) regions. The maximum temperatures increased in the western study area, whereas the minimum temperatures increased more significantly in the Heihe River Basin and Shiyanghe River Basin. All temperature extremes displayed trends consistent with warming, except for warmest-night temperature (TNn) and coldest-day temperature (TXn). More warming occurred mainly in higher-altitude areas and desert areas, and the greater warming of both cold extremes and warm extremes occurred at night rather than during the day. In addition, an altitude dependence indicated greater warming in higher-altitude regions, which was particularly evident from the temperature extremes.
Precipitation slowly increased during the study period. Amount of precipitation and number of rainy days increased mainly in the Qilian Mountains and Hexi Corridor, whereas other regions exhibited decreasing trends, particularly the Badain Jaran Desert and the downstream areas of the Shulehe and Heihe River basins. Similar to temperature extremes, the significance of changes in precipitation extremes during 1960-2011 was also high except for maximum 5-day precipitation (RX5day), simple daily intensity index (SDⅡ), and consecutive wet days (CWD). Precipitation and precipitation extremes were statistically correlated with altitude, and indicated more precipitation and precipitation extremes in higher-altitude regions. These changes in temperature and precipitation can be useful for establishing better management strategies for water resources. Further studies of the impact of these changes on river runoffs and glaciers in the region are urgently needed.
Acknowledge:This study was supported by the Key Project of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (KZZD-EW-04-05), a Key Project of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (30970492, 31270489, 31270482), and a Project for Incubation of Specialists in Glaciology and Geocryology of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (11J0930003).
| Aguilar E, Barry AA, Brunet M, 2009. Changes in temperature and precipitation extremes in western central Africa, Guinea Conakry, and Zimbabwe, 1955-2006. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 114(D2): 356–360. doi: 10.1029/2008jd011010 |
| Aguilar E, Peterson TC, Obando PR, et al, 2005. Changes in precipitation and temperature extremes in Central America and northern South America, 1961-2003. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 110(D23): 3233–3250. doi: 10.1029/2005JD006119 |
| Alexander LV, Zhang X, Peterson TC, et al, 2006. Global observed changes in daily climate extremes of temperature and precipitation. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 111(D5): 1042–1063. doi: 10.1029/2005JD006290 |
| Chen SY, Dong AX, Han T, 2007. Differences in summer precipitation between the east and west of the Qilian Mountains and its contributing factors. Journal of Nanjing Institute of Meteorology, 30(5): 715–719. |
| Cheng AF, Feng Q, Fu GB, et al, 2015. Recent changes in precipitation extremes in the Heihe River Basin, Northwest China. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 32: 1391–1406. doi: 10.1007/s00376-015-4199-3 |
| China Meteorological Administration, 2006. Climate and Environment in China. Beijing: Meteorology Press. |
| Ding YJ, Ye BS, Liu SY, 2000. Impact of climate change on the alpine streamflow during the past 40 a in the middle part of the Qilian Mountains, Northwestern China. Journal of Glaciolgy & Geocryology, 22(3): 193–199. |
| Easterling DR, Meehl GA, Parmesan C, et al, 2000. Climate extremes: Observations, modeling, and impacts. Science, 289(5487): 2068–2074. doi: 10.1126/science.289.5487.2068 |
| Feng Q, Ma H, Jiang XM, et al, 2015. What has caused desertification in China. Scientific Reports, 5: 1–8. doi: 10.1038/srep15998 |
| Feng Qi, Li ZX, Liu W, et al, 2016. Relationship between large scale atmospheric circulation, temperature and precipitation in the Extensive Hexi region, China, 1960-2011. Quaternary International, 392: 187–196. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2015.06.015 |
| Haylock MR, Peterson TC, Alves LM, et al, 2006. Trends in total and extreme South American rainfall in 1960-2000 and links with sea surface temperature. Journal of Climate, 19(8): 1490–1512. doi: 10.1175/jcli3695.1 |
| Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), 2007. The Physical Science Basis. UK: Cambridge University Press. |
| Jia WX, He YQ, Li ZX, et al, 2008a. The regional difference and catastrophe of climatic change in Qilian Mt. region. Acta Geographica Sinica, 63(3): 257–269. |
| Jia WX, He YQ, Li ZX, et al, 2008b. Spatio-temporal distribution characteristics of climate change in Qilian Mountains and Hexi Corridor. Journal of Desert Research, 28(6): 1151–1156. |
| Klein Tank AMG, Peterson TC, Quadir DA, et al, 2006. Changes in daily temperature and precipitation extremes in central and south Asia. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 111(D16): 709–720. doi: 10.1029/2005jd006316 |
| Li L, Wang ZY, Wang QC, 2006. Inflence of climatic change on flow over the upper reaches of Heihe River. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 26(1): 40–46. |
| Li ZX, Feng Q, Liu W, et al, 2015b. The stable isotope evolution in Shiyi glacier system during the ablation period in the north of Tibeteau, China. Quaternary International, 347: 93–109. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2015.02.013 |
| Li ZX, He YQ, An WL, et al, 2011. Climate and glacier change in southwestern China during the past several decades. Environmental Research Letters, 6(4): 45404–45427. doi: 10.1088/1748-9326/6/4/045404 |
| Li ZX, Feng Q, Li J, et al, 2015a. Environmental significance and hydrochemical processes at a cold alpine basin in the Qilian Mountains. Environmental Earth Sciences, 73(8): 4043–4052. doi: 10.1007/s12665-014-3689-4 |
| Li ZX, He YQ, Theakstone WH, et al, 2012a. Altitude dependency of trends of daily climate extremes in southwestern China, 1961-2008. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 22(3): 416–430. doi: 10.1007/s11442-012-0936-z |
| Li ZX, He YQ, Wang PY, et al, 2012b. Changes of daily climate extremes in southwestern China during 1961-2008. Global and Planetary Change, 80(1): 255–272. doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2011.06.008 |
| Liu BH, Xu M, Henderson M, et al, 2005. Observed trends of precipitation amount, frequency, and intensity in China, 1960-2000. Journal of Geophysical Research Atmospheres, 110. doi: 10.1029/2004JD004864 |
| Liu XD, Cheng ZG, Yan LB, et al, 2009. Elevation dependency of recent and future minimum surface air temperature trends in the Tibetan Plateau and its surroundings. Global & Planetary Change, 68(3): 164–174. doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2009.03.017 |
| New M, Hewitson B, Stephenson DB, et al, 2006. Evidence of trends in daily climate extremes over southern and west Africa. Journal of Geophysical Research Atmospheres, 111(D14): 3007–3021. doi: 10.1029/2005JD006289 |
| Peterson TC, Taylor MA, Demeritte R, et al, 2002. Recent changes in climate extremes in the Caribbean region. Journal of Geophysical Research Atmospheres, 107(D21). doi: 10.1029/2002JD002251 |
| Pu JC, Yao TD, Wang NL, et al, 2004. Fluctuations of the glaciers on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau during the past century. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 26(5): 517–522. |
| Shi YF, 2001. Estimation of the water resources affected by climatic warming and glacier shrinkage before 2050 in West China. Journal of Glaciolgy and Geocryology, 23(4): 333–341. |
| Shi YF, 2003. Discussion on the present climate change from warm-dry to warm-wet in Northwest China. Quaternary Sciences, 23(2): 152–164. |
| Shi YF, Shen YP, Hu RJ, 2002. Preliminary study on signal, impact and foreground of climatic shift from warm-dry to warm-humid in Northwest China. Journal of Glaciolgy and Geocryology, 24(3): 219–226. |
| Sun MP, Liu SY, Yao XJ, et al, 2015. Glacier changes in the Qilian Mountains in the past half century: Based on the revised First and Second Chinese Glacier Inventory. Acta Geographica Sinica, 70(9): 1402–1414. |
| Tang MC, 1985. The distribution of precipitation in Mountain Qilian. Acta Geographica Sinica, 40(4): 323–332. |
| Wang PY, Li ZQ, Gao WY, 2011a. Rapid shrinking of glaciers in the middle Qilian Mountain region of Northwest China during the last ~50 years. Journal of Earth Science, 22(4): 539–548. doi: 10.1007/s12583-011-0195-4 |
| Wang PY, Li ZQ, Li HL, et al, 2011b. Ice surface-elevation change and velocity of Qingbingtan Glacier No. 72 in the Tomor region, Tianshan Mountains, central Asia. Journal of Mountain Science, 8(6): 855–864. doi: 10.1007/s11629-011-1018-x |
| Wang PY, Li ZQ, Li HL, et al, 2012. Glacier No. 4 of Sigong River over Mt. Bogda of eastern Tianshan, central Asia: thinning and retreat during the period 1962-2009. Environmental Earth Sciences, 66(1): 265–273. doi: 10.1007/s12665-011-1236-0 |
| Wang YM, Feng Q, Kang XC, 2016. Tree-ring based reconstruction of temperature variability (1445-2011) for the upper reaches of the Heihe River Basin, Northwestern China. Journal of Arid Land, 8(1): 60–76. doi: 10.1007/s40333-015-0138-5 |
| Yao TD, Wang YQ, Liu SY, et al, 2004. Recent glaciers retreating in High Asia and their impact on the water resources of Northwest China. Science in China Series D (Earth Scieces), 34(6): 535–543. doi: 10.1360/03yd0256 |
| Ye BS, Li C, Yang DQ, et al, 2004. Variation trend of precipitation and its impact on water resources in China during last 50 years (I): annual variation. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 26(5): 587–594. |
| Yin XZ, Zhang Q, Xu QY, et al, 2009. Characteristics of climate change in Qilian Mountains region in recent 50 years. Plateau Meteorology, 28(1): 85–90. |
| You QL, Kang SC, Aguilar E, et al, 2011. Changes in daily climate extremes in China and their connection to the large scale atmospheric circulation during 1961-2003. Climate Dynamics, 36: 11–12. doi: 10.1007/s00382-009-0735-0 |
| Zhang CJ, Guo N, 2002. Climatic variation characteristics over Qilian Mountain area during the last 40 years. Meteorological Monthly, 28(12): 33–39. |
| Zhang L, Wang SG, Shang KZ, et al, 2007. Research on vapor and precipitation resources over the Qilian Mountain area. Arid Meteorology, 25(1): 14–20. |
| Zhang XB, Aguilar E, Sensoy S, et al, 2005. Trends in Middle East climate extreme indices from 1950 to 2003. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 110(D22): 3159. doi: 10.1029/2005jd006181 |
 2016, 8
2016, 8

